What is a High Efficiency Condensing Boiler?
- Matt Mercer
- Aug 5, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 6, 2025
A person with minimal experience in the HVAC business has more than likely heard the term High Efficiency Condensing Boiler (HECB). If you are unfamiliar with the differences between a Standard Efficiency boiler (SEB) and a HECB are as follows:
A (SEB) is designed to operate in the 80% - 85% efficiency range of heat transfer for heating building spaces and/or domestic water. This is achieved by utilizing a single pass or two-pass heat exchanger, usually constructed of cast iron section or finned copper tubes. A pass is how many times the heated medium and the combustion products cross paths.
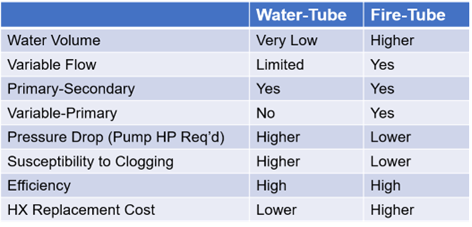
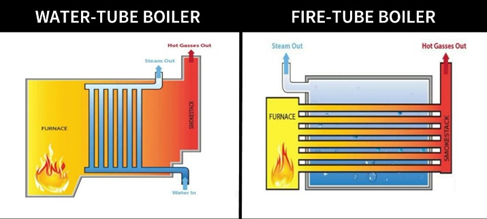
The primary difference between a SEB and a HECB is the heat exchanger materials of construction. To extract as much heat as possible from the fuel source, the heat exchanger design should utilize more than a single or two-pass design. As the heat is extracted from the gas flame and associated flue, the flue temperature lowers as it leaves the boiler. When the temperature drops below the due point of the water vapor in the flue gases (ideally 135 ֯ F) condensing occurs, but acids are the byproduct of this process. These acids are highly corrosive requiring heat exchangers to be constructed of corrosion resistant materials, such as aluminum or stainless steel. The cooler flue gases, are a sign that efficient heat transfer is occurring, saving more energy in the process. HECB achieve combustion efficiencies in the range of 88% - 95%, so the lower the return water temperature to the boiler the better efficiency!
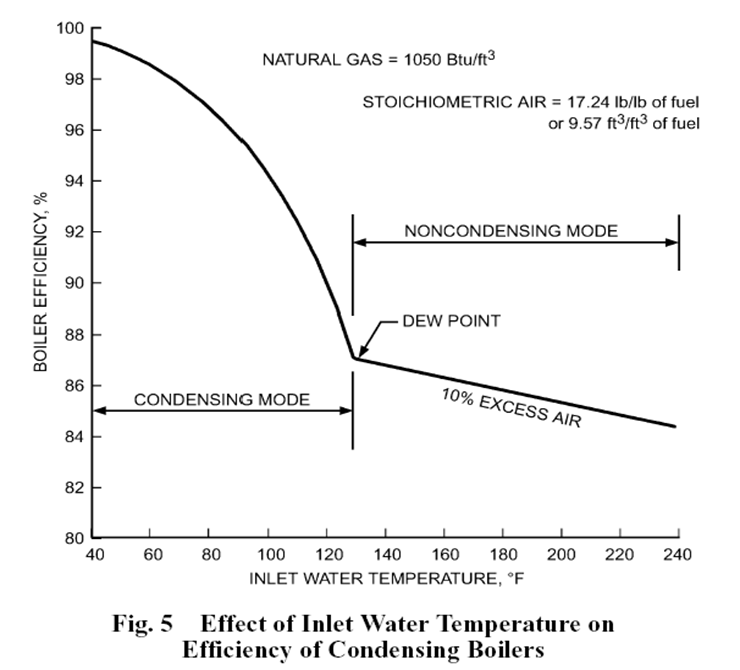
In modern hydronic system designs, anything that requires energy must adhere to high efficiency standards and boilers are not exempt from this requirement. Soon the SEB will be a thing of the past. Therefore, two questions we should be asking, are, “How to best use HECB in new construction and in retrofit applications?”. There are many existing systems in need of redesigned under new efficiency guidelines. There are lots of points to consider when installing HECB on a system designed for a SEB.
This is one article of four. Please come back for “PART 2 - Design Considerations for High Efficiency Condensing Boiler Systems”






Comments